Example 2: HackerNews clone #
Let’s create a real world web application base on the login system we created! We are going to create a minimal HackerNews clone:
- User can create account, login, logout (we’ve finished it before!)
- Signed in user can submit a link and a title
- User can edit/delete the submitted link that created by their own.
After this example, you will learn:
- How to use react-query’s
Query Invalidationin real world application - How to secure API routes
Form for submitting link #
f84d8006e31
Before creating the form for submitting link, let’s create a navigation bar: If user has logged in, show his username and a logout link. Otherwise show a login link:
// pages/index.tsx
import React from 'react'
import { getUserFromReq } from '../utils.server'
function IndexPage(props: {
user?: {
name: string
}
}) {
return (
<>
<div>
{props.user ? <>
<span>Hi, {props.user.name}, </span>
<a href="/api/logout">Logout</a>
</> : <>
<a href="/login">Login</a>
</>}
</div>
</>
)
}
export async function getServerSideProps(ctx) {
const user = await getUserFromReq(ctx.req)
return {
props: {
user: user ? { name: user?.name } : null
}
}
}
export default IndexPage
To determine if user has logged in, we get the current user’s info in getServerSideProps, and pass it to the client page props. So in the page we can know the user hasn’t logged in if the props.user is null.
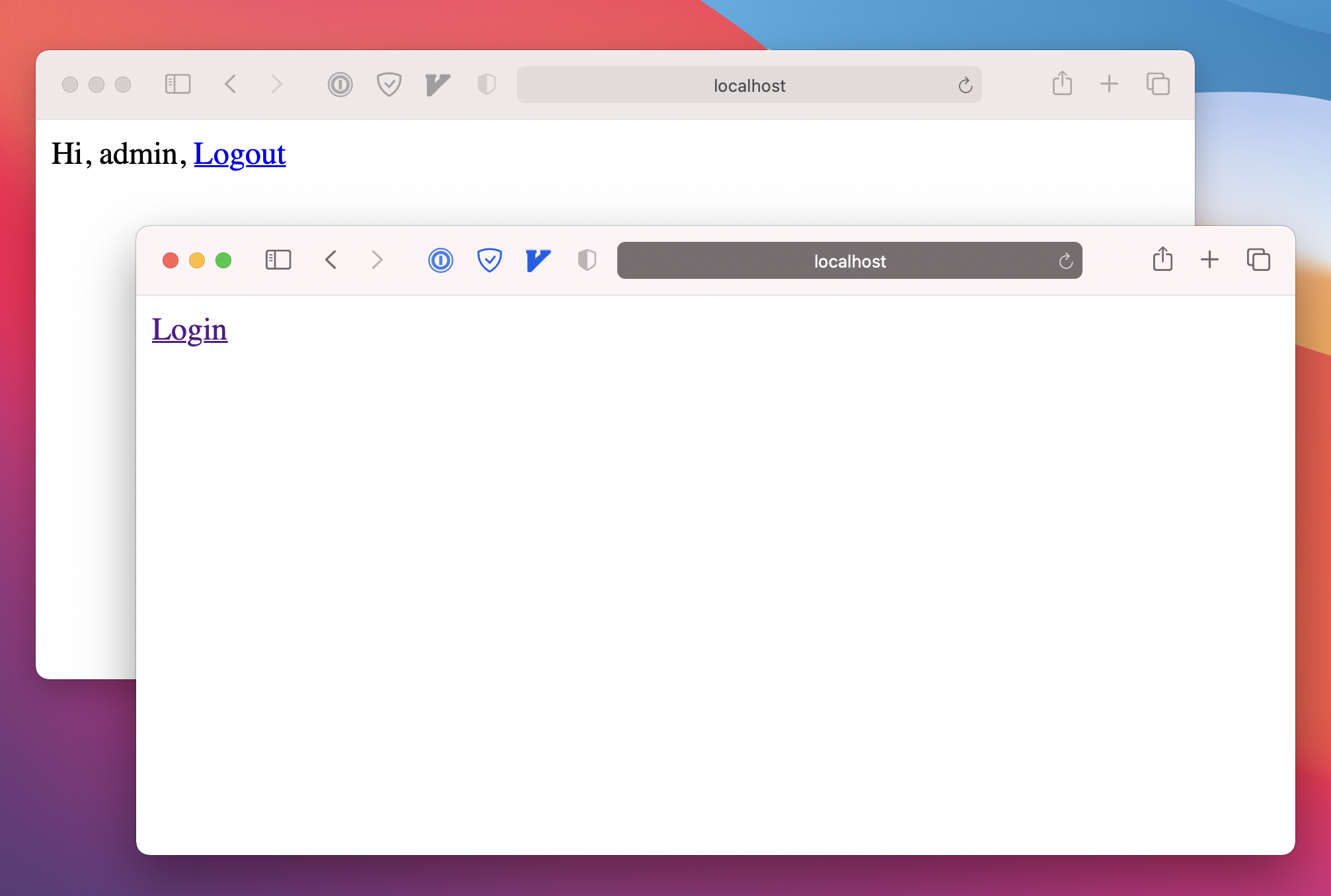
Then let’s create a form for submitting link. This form is only visible for the user who has logged in.
// pages/index.tsx
function SubmitLinkForm() {
return (
<>
<h2>Submit link</h2>
<div>
<label>URL: </label>
<input type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<label>Title: </label>
<input type="text" />
</div>
</>
)
}
function IndexPage(props: {
user?: {
name: string
}
}) {
return (
<>
<div>
{props.user ? <>
<span>Hi, {props.user.name}, </span>
<a href="/api/logout">Logout</a>
</> : <>
<a href="/login">Login</a>
</>}
</div>
{/* Only signed in user can see the submit link form */}
{props.user && <div>
<SubmitLinkForm />
</div>}
</>
)
}
Data model #
51282d8145347
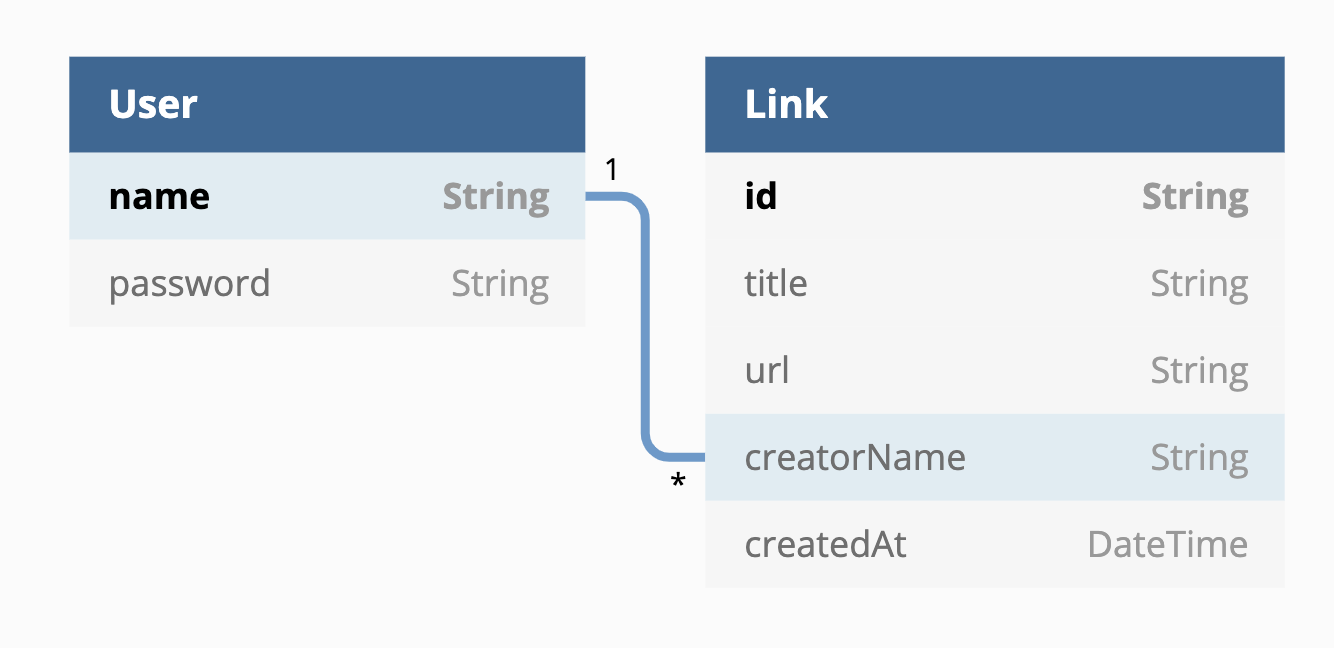
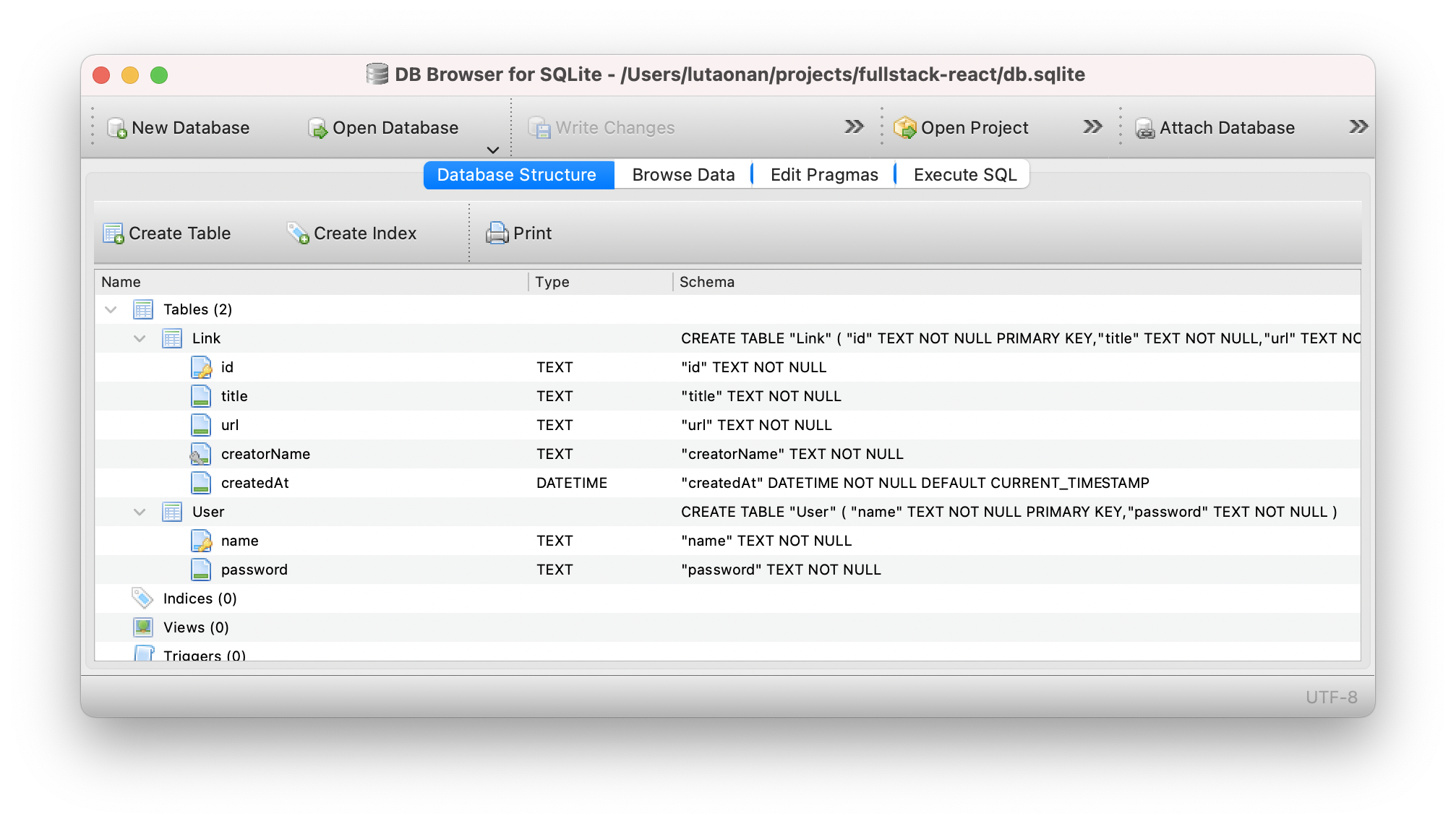
User can submit link, so we should have a Link table. Every link has title and url.
Because very link is created by a user, there should be a foreign key creatorName point to User’s name.
Here is how we declare the data model in Prisma Schema (prisma/schema.prisma):
model User {
name String @id
password String
links Link[] @relation("link_creator")
}
model Link {
id String @id @default(uuid())
title String
url String
creatorName String
creator User @relation(name: "link_creator", fields: [creatorName], references: [name])
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
}
Then run yarn prisma db push to apply this schema to the database.
(Secured) API for submitting link #
35b7bc1407
Now we create a POST /api/link for user to submit a link in home page.
// pages/api/link
import { apiHandler, prisma } from "../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.post(async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
url: string,
title: string
}
await prisma.link.create({
data: {
url: body.url,
title: body.title,
// TODO: how to get creator's username
// creatorName: ''
}
})
res.json({
message: 'Success'
})
})
In this POST handler, we receive a url and title in the request body. Then create a link record in Link table, by prisma.link.create.
But the code wasn’t finished. Because we need to provide the username of the user who submit this link, which is the current logged in user.
How can we get current logged in user in api route? Since we use next-connect, we can write a middleware that inject the current logged in user into the req object. But if a non logged in user POST this API, we just response a 403.
We can write this middleware in utils.server.ts:
// utils.server.ts
export const authMiddleware = () => async (req, res, next) => {
const user = await getUserFromReq(req)
if (!user) {
throw Boom.forbidden('Please login first')
} else {
req.user = user
next()
}
}
Then use it on api route:
import { apiHandler, authMiddleware, prisma } from "../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
+ .post(authMiddleware(), async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
url: string,
title: string
}
+ const user = req.user
await prisma.link.create({
data: {
url: body.url,
title: body.title,
+ creatorName: user.name
}
})
res.json({
message: 'Success'
})
})
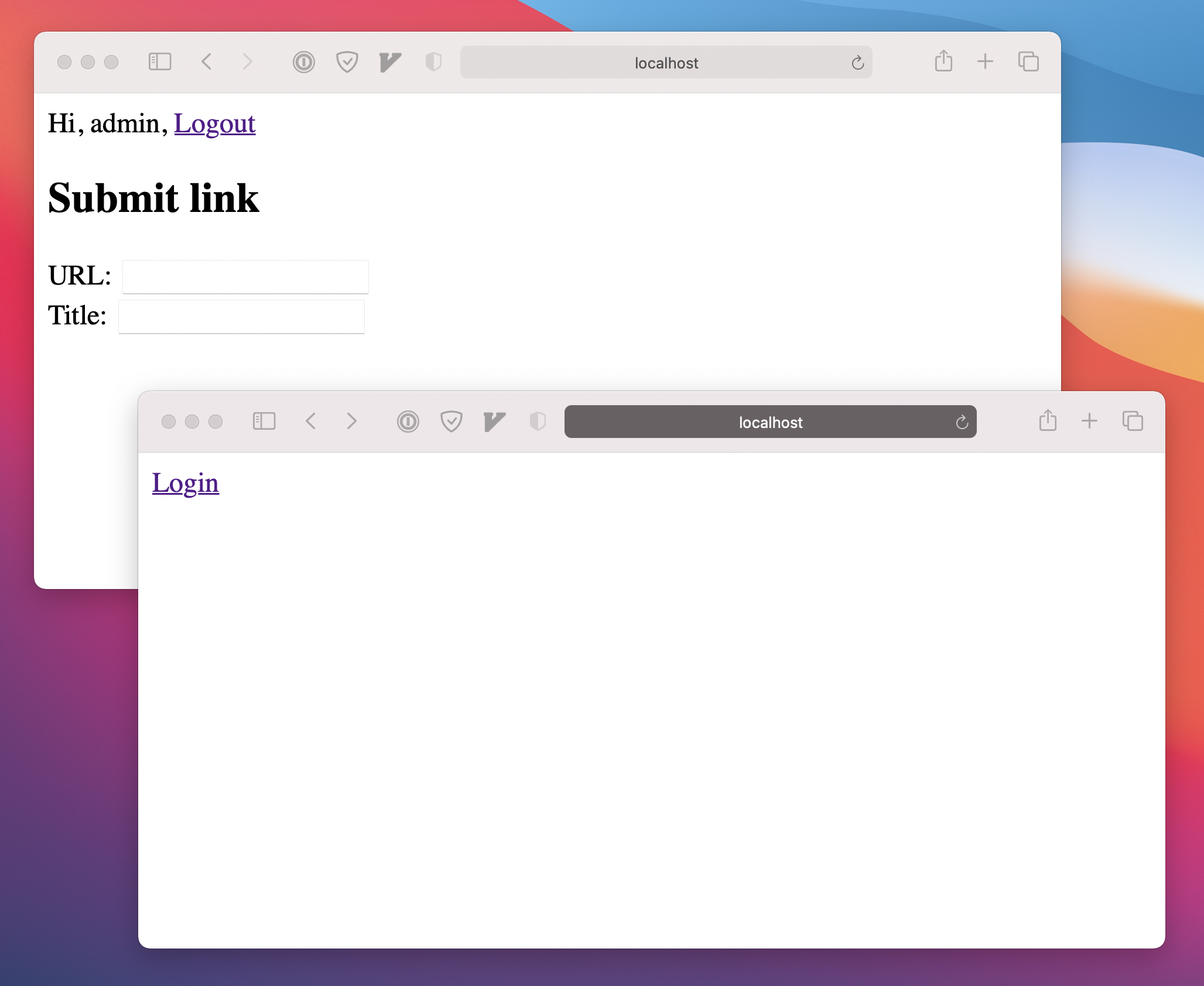
Now, if a non logged in user POST this api, he will get a 403 response:
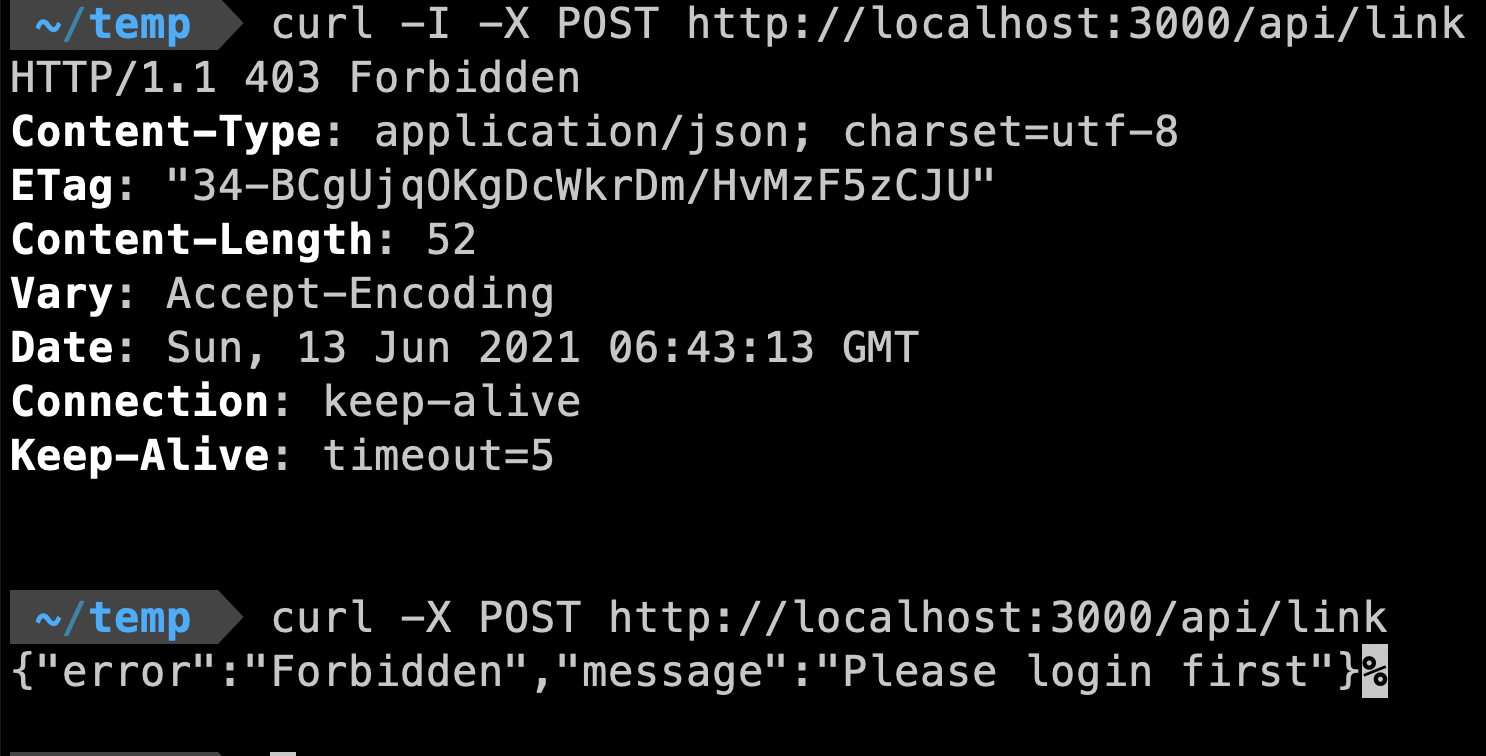
We can reuse the authMiddleware() in any other api route that need to be secured.
Fetch/Submit links #
1406f062d3f
Now, let’s fetch and display all the links on page /. Firstly, we need to create a GET /api/link api to get all links. In /pages/api/link.ts , let’s add a .get() handler:
// pages/api/link.ts
import { apiHandler, authMiddleware, prisma } from "../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.get(async (req, res) => {
const links = await prisma.link.findMany({
orderBy: {
createdAt: 'desc'
}
})
res.json({
data: links
})
})
.post(authMiddleware(), async (req, res) => {
// ......
})
We use findMany() to query all links, and sort them by createdAt.
This route is accessible by everyone, so we don’t use authMiddleware().
Now in home page /, add a query to fetch all links:
// pages/index.tsx
// the query method
async function fetchAllLinks() {
const result = await axios.get(`/api/link`)
return result.data.data
}
function IndexPage(props: {
user?: {
name: string
}
}) {
const fetchAllLinksQuery = useQuery('fetchAllLinks', fetchAllLinks)
return (
<>
<div>
{props.user ? <>
<span>Hi, {props.user.name}, </span>
<a href="/api/logout">Logout</a>
</> : <>
<a href="/login">Login</a>
</>}
</div>
{/* Only signed in user can see the submit link form */}
{props.user && <div>
<SubmitLinkForm />
</div>}
{/* fetch all links and render them */}
<div>
{fetchAllLinksQuery.isLoading && <div>Loading...</div>}
{fetchAllLinksQuery.data?.map(link => {
return (
<div key={link.id}>
<a href={link.url}>{link.title}</a>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</>
)
}
It’s time to implement the submit link mutation now!
// pages/index.tsx
async function submitLink(body: {
title: string,
url: string
}) {
await axios.post(`/api/link`, body)
}
function SubmitLinkForm() {
const $title = React.useRef(null)
const $url = React.useRef(null)
const submitLinkMutation = useMutation(submitLink, {
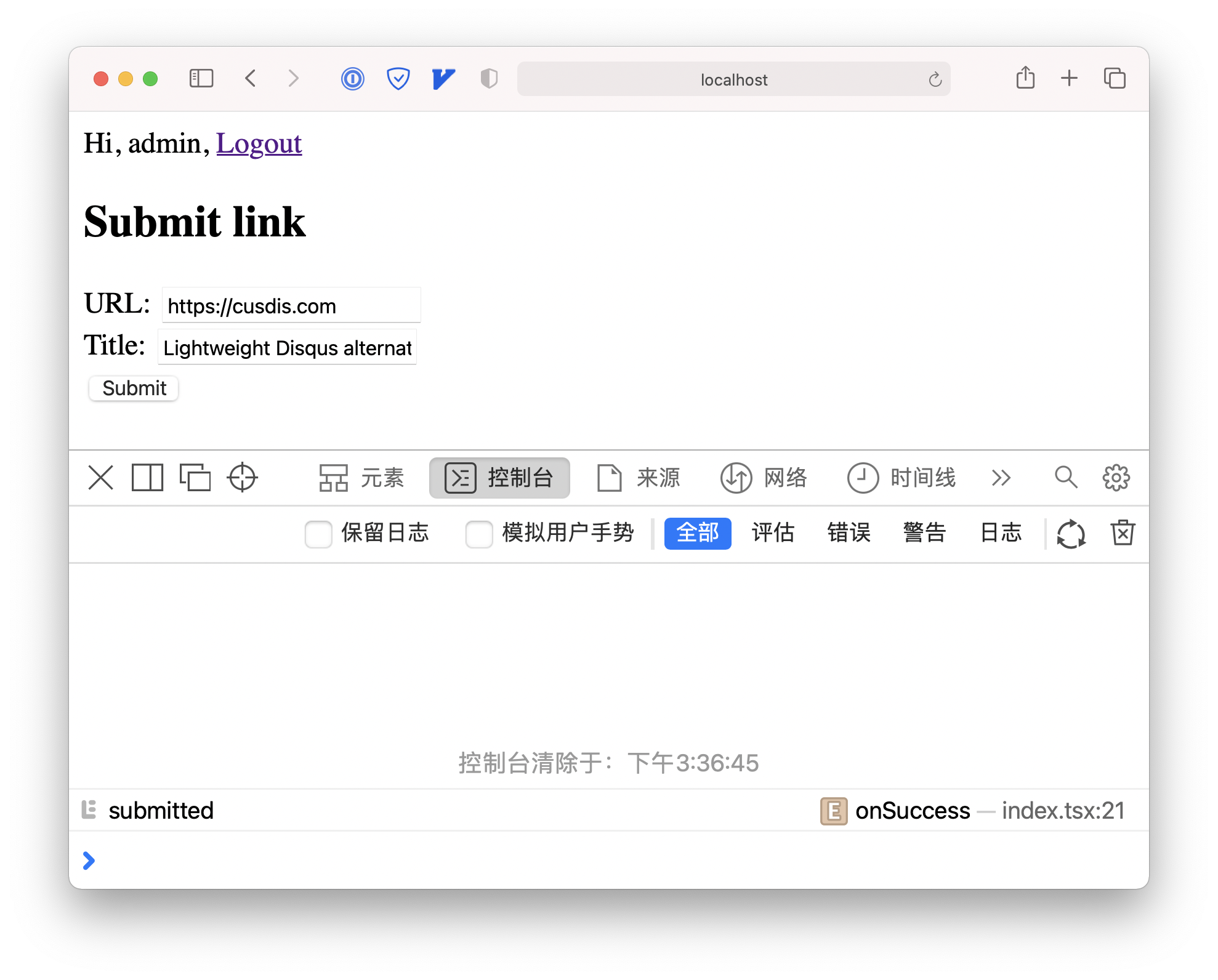
onSuccess() {
console.log('submitted!')
}
})
function onClickSubmit() {
submitLinkMutation.mutate({ title: $title.current.value, url: $url.current.value })
}
return (
<>
<h2>Submit link</h2>
<div>
<label>URL: </label>
<input ref={$url} type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<label>Title: </label>
<input ref={$title} type="text" />
</div>
<button disabled={submitLinkMutation.isLoading} onClick={onClickSubmit}>Submit</button>
</>
)
}
When submitLinkMutation success, we log submitted:
But what if we want the user can see the latest links instantly after he submitting the new link? We can use the Query Invalidation technique of react-query. Remember how we fetch all the links?
const fetchAllLinksQuery = useQuery('fetchAllLinks', fetchAllLinks)
We gave this query a key fetchAllLinks. So we can use queryClient.invalidateQueries('fetchAllLinks') to mark this query as stale. Then react-query will refetch this query for us:
// pages/index.tsx
+ import { queryClient } from './_app'
const $title = React.useRef(null)
const $url = React.useRef(null)
const submitLinkMutation = useMutation(submitLink, {
onSuccess() {
- console.log('submitted!')
+ queryClient.invalidateQueries('fetchAllLinks')
}
})
function onClickSubmit() {
submitLinkMutation.mutate({ title: $title.current.value, url: $url.current.value })
}
Now when user submits new link, the links list will be refreshed.
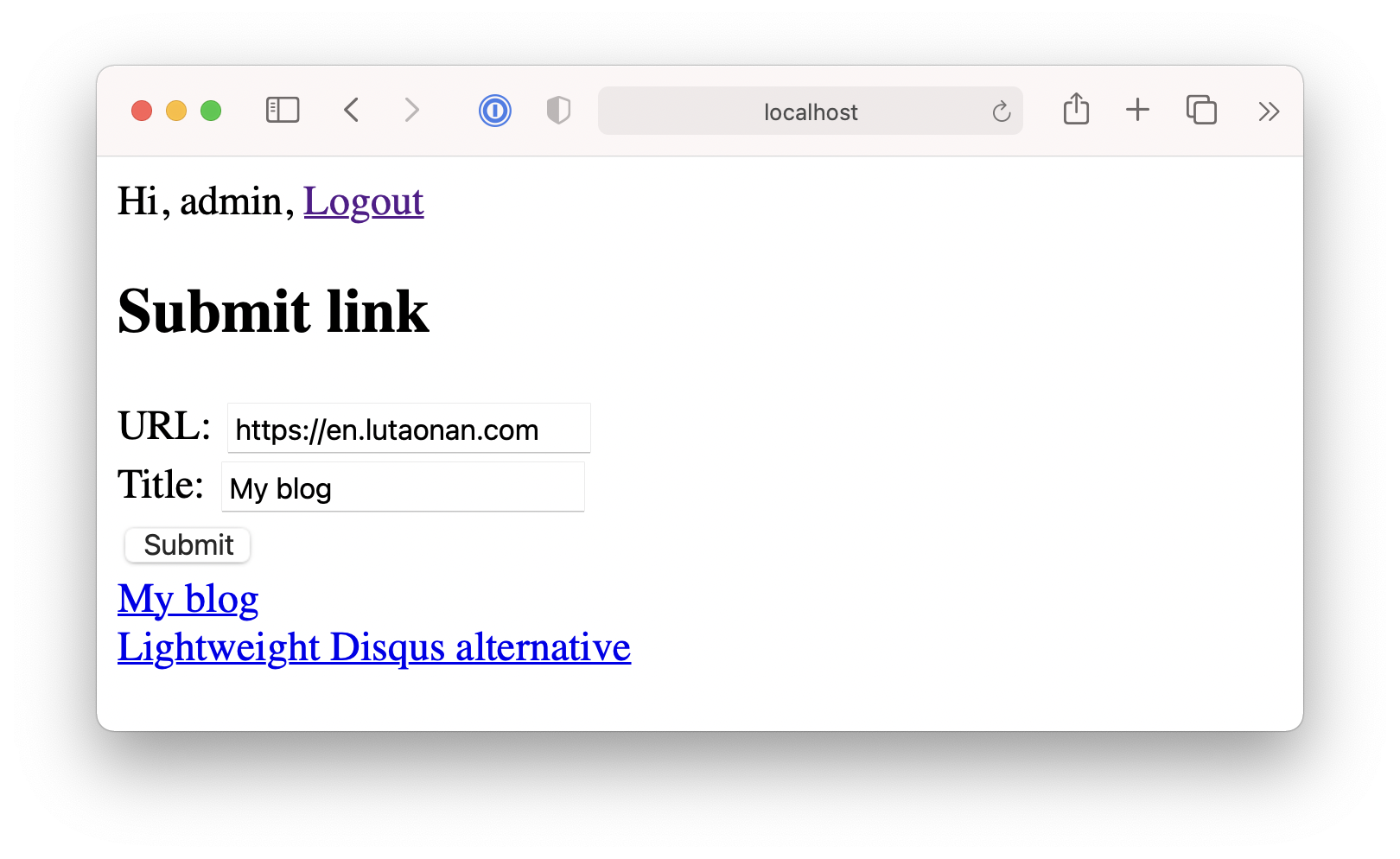
Edit links #
607310047a29cc0f
User can edit or delete links that are created by their own.
To create an API for editing a link, the path would be PUT /api/link/:linkId. In Next.js, we can create a dynamic route by creating a file /pages/api/link/[linkId]/index.ts. In the route handler, we can use req.query.linkId to get the route params. For example:
// pages/api/link/[linkId]/index.ts
import { apiHandler } from "../../../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.put(async (req, res) => {
res.send(req.query.linkId)
})
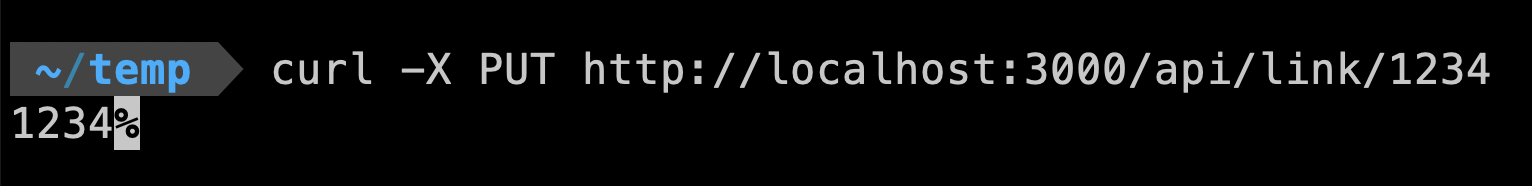
To edit a link, we need to receive the title or url in the request body, and use prisma.link.update() to update the record:
// pages/api/link/[linkId]/index.ts
import { apiHandler, prisma } from "../../../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.put(async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
title?: string,
url?: string
}
const linkId = req.query.linkId as string
await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: linkId
},
data: {
title: body.title,
url: body.url
}
})
res.json({
message: 'success'
})
})
But it’s not finished. We have to secure this api: only the link that created by the current logged in user can edit the link.
We can use the authMiddleware() here to prevent non logged in user, and determine if the link’s creatorName is equal to logged in user’s username:
import Boom from "@hapi/boom";
import { apiHandler, authMiddleware, prisma } from "../../../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.put(authMiddleware(), async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
title?: string,
url?: string
}
const linkId = req.query.linkId as string
// get current logged in user's information
const user = req.user
// get link's information
const link = await prisma.link.findUnique({
where: {
id: linkId
}
})
// check the link's creator is current logged in user. If not, response a 403 error
if (link.creatorName !== user.name) {
throw Boom.forbidden('Permission Denined!')
}
await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: linkId
},
data: {
title: body.title,
url: body.url
}
})
res.json({
message: 'success'
})
})
But you know what? We can extract this secure code to a dedicated middleware for checking if the request user is the creator of the link. It can be reused in the delete api that we will implement later.
Define a linkCreatorGuard() in utils.server.ts :
// utils.server.ts
export const linkCreatorGuard = (getLinkId: (req) => string) => async (req, res, next) => {
const user = req.user
const linkId = getLinkId(req)
const link = await prisma.link.findUnique({
where: {
id: linkId
},
select: {
creatorName: true
}
})
if (user.name !== link.creatorName) {
throw Boom.forbidden('Permission Denined')
} else {
next()
}
}
This is a function that receives a function for getting link id from the request, then return a middleware. Let’s see how to use it in the PUT handler:
import { apiHandler, authMiddleware, linkCreatorGuard, prisma } from "../../../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.put(
authMiddleware(),
linkCreatorGuard(req => req.query.linkId),
async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
title?: string,
url?: string
}
await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: req.query.linkId
},
data: {
title: body.title,
url: body.url
}
})
res.json({
message: 'success'
})
})
We pass a req => req.query.linkId as the first param to tell the linkCreatorGuard what the link’s id is. Because linkCreatorGuard depends on req.user, it needs to be used after the authMiddlware().
Now, create the link edit form for each link in the page:
// pages/index.tsx
import { Link } from '@prisma/client'
import { queryClient } from './_app'
const editLink = (linkId: string) => async (body: {
title?: string,
url?: string
}) => {
await axios.put(`/api/link/${linkId}`, body)
}
function EditLinkForm(props: {
link: Link
}) {
const $title = React.useRef(null)
const $url = React.useRef(null)
const editLinkMutation = useMutation(editLink(props.link.id), {
onSuccess() {
// mark `fetchAllLinks` query as stale after editing a link
queryClient.invalidateQueries('fetchAllLinks')
},
onError(err) {
// if error, alert the error message
alert(err.response.data.message)
}
})
function onClickSave() {
editLinkMutation.mutate({ title: $title.current.value, url: $url.current.value })
}
return (
<>
<div>
<label>URL: </label>
<input defaultValue={props.link.url} ref={$url} type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<label>Title: </label>
<input defaultValue={props.link.title} ref={$title} type="text" />
</div>
<button disabled={editLinkMutation.isLoading} onClick={onClickSave}>Save</button>
</>
)
}
It’s almost the same as the form for submitting link. When the link is edited, we call queryClient.invalidateQueries('fetchAllLinks') to mark fetchAllLinks as stale too.
Let’s put this EditLinkForm below every link:
function IndexPage(props: {
user?: {
name: string
}
}) {
const fetchAllLinksQuery = useQuery('fetchAllLinks', fetchAllLinks)
return (
<>
<div>
{props.user ? <>
<span>Hi, {props.user.name}, </span>
<a href="/api/logout">Logout</a>
</> : <>
<a href="/login">Login</a>
</>}
</div>
{/* Only signed in user can see the submit link form */}
{props.user && <div>
<SubmitLinkForm />
</div>}
<div>
{fetchAllLinksQuery.isLoading && <div>Loading...</div>}
{fetchAllLinksQuery.data?.map(link => {
return (
<div style={{ marginTop: '1rem' }}>
<div key={link.id}>
- <a href={link.url}>{link.title}</a>
+ <a href={link.url}>{link.title}</a> <span>by: {link.creatorName}</span>
</div>
<div>
+ <EditLinkForm link={link} />
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</>
)
}
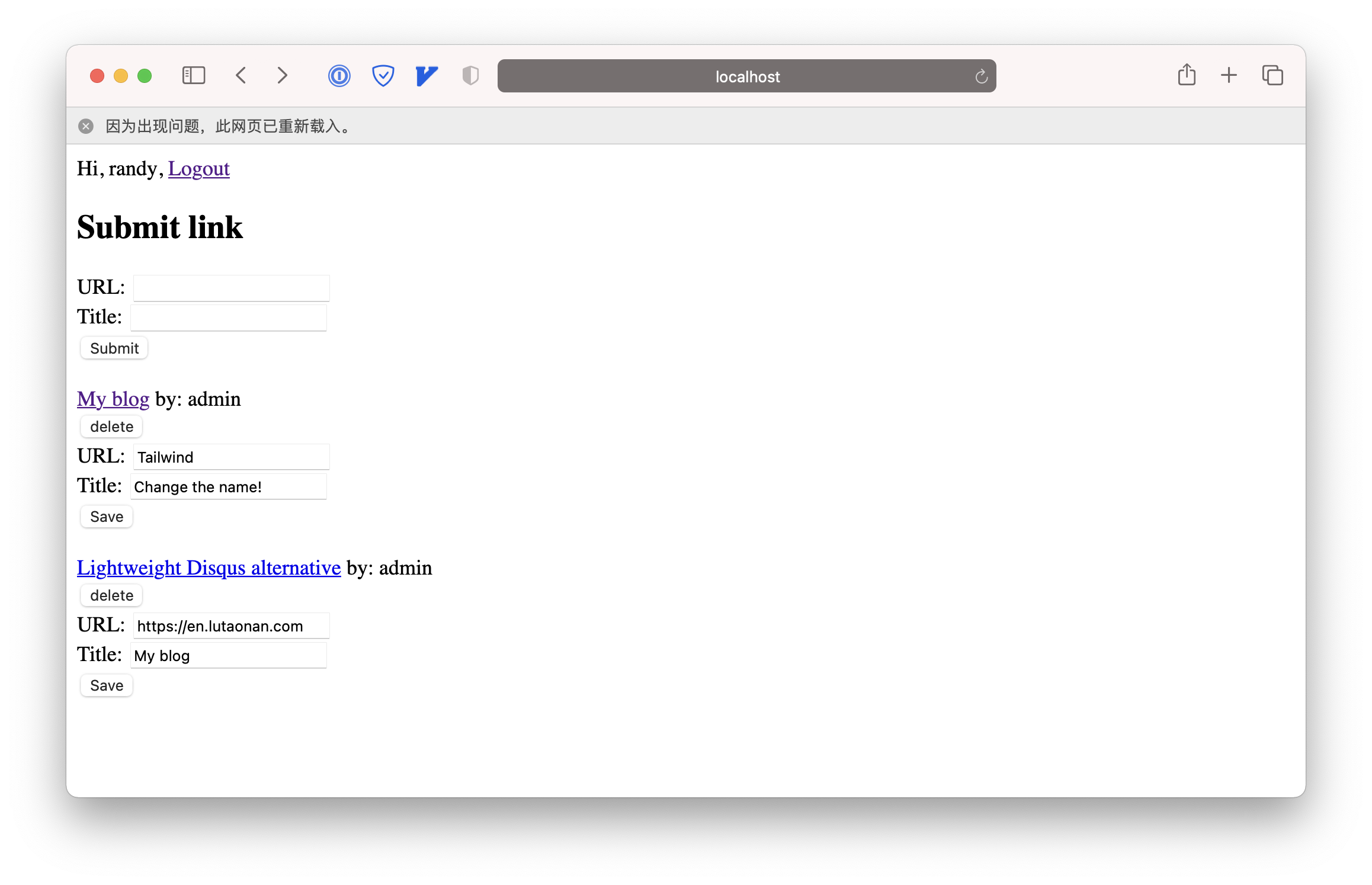
We also display the link.creatorName next to the link title. The home page now has became like this:
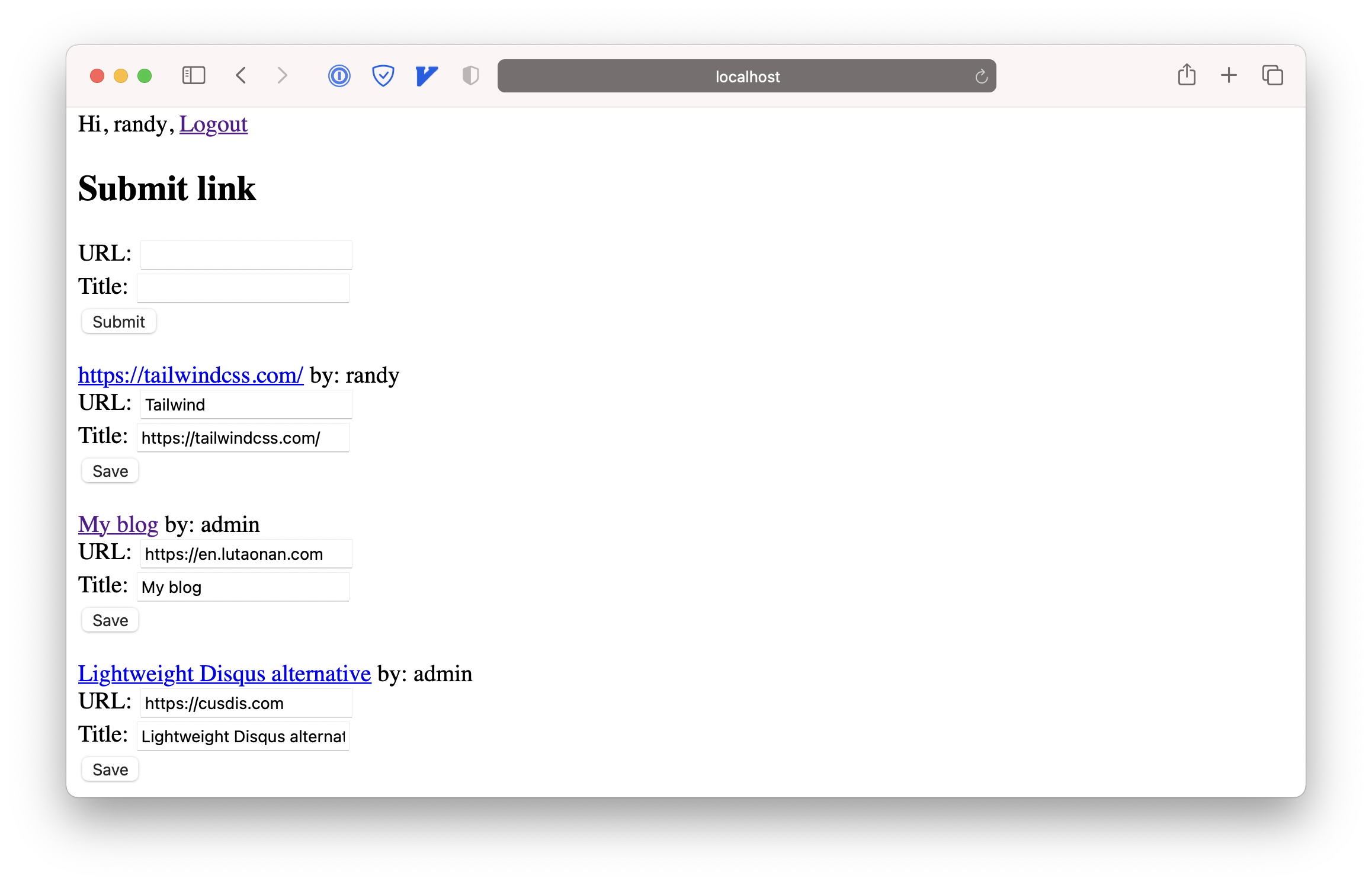
Now, let’s try to test if the user can edit the link that wasn’t created by their own. I’m now login as randy, let me edit the link created by admin:
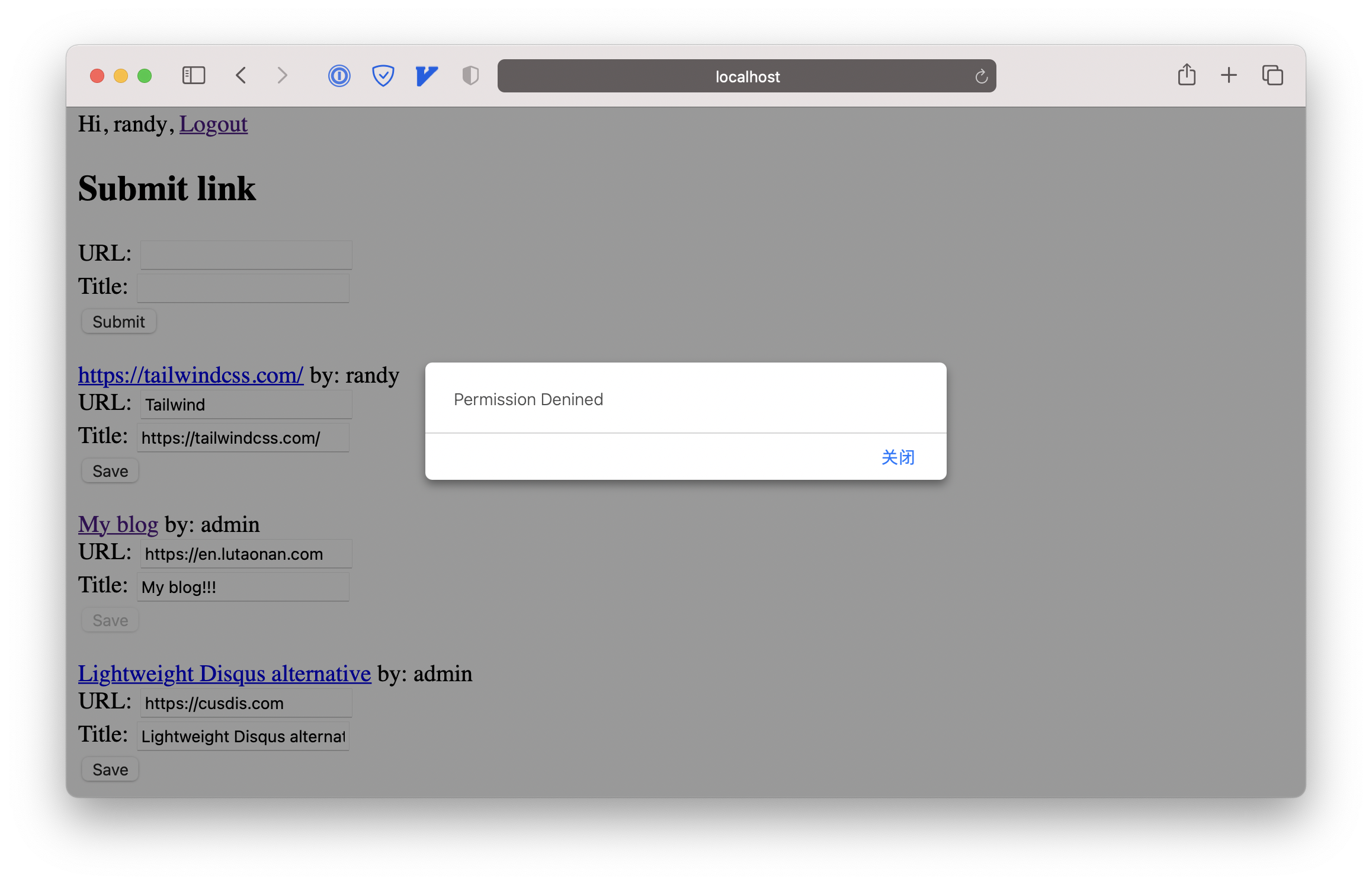
Great! It means the linkCreatorGuard works! Now try to edit the link that created by myself. It works well too. And I can see the change immediately after the PUT request succeeding.
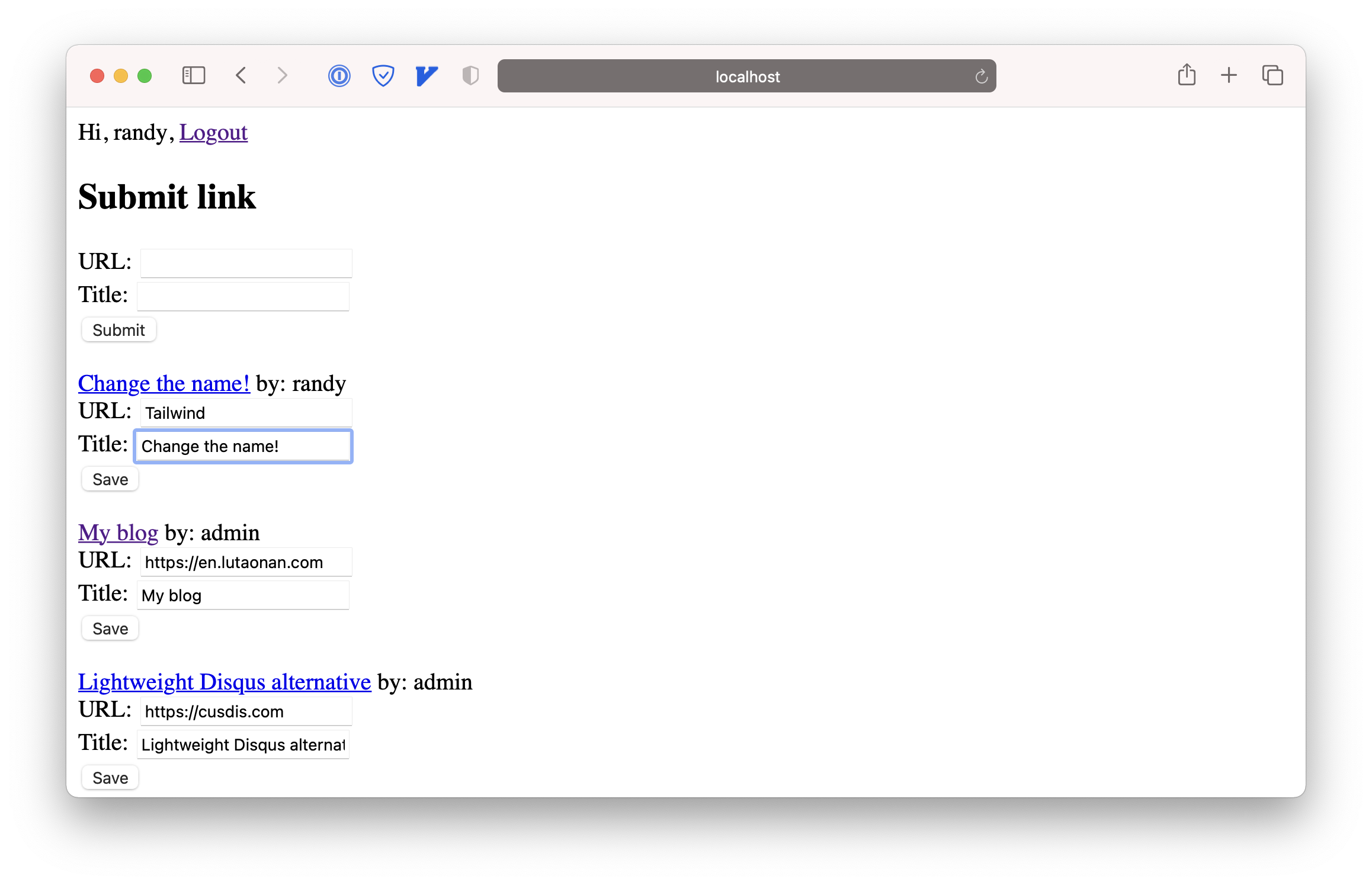
Delete links #
f64677053742f
Implementing delete links is quite easy now because we almost have done everything in previous section and we make them very reusable. To create a secured delete link api DELETE /api/link/:linkId, just create an api route handler and use authMiddleware() and linkCreatorGuard():
// pages/api/link/[linkId]/index.ts
import {
apiHandler,
authMiddleware,
linkCreatorGuard,
prisma,
} from "../../../../utils.server";
export default apiHandler()
.put(
authMiddleware(),
linkCreatorGuard((req) => req.query.linkId),
async (req, res) => {
const body = req.body as {
title?: string;
url?: string;
};
await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: req.query.linkId,
},
data: {
title: body.title,
url: body.url,
},
});
res.json({
message: "success",
});
}
)
// delete a link
.delete(
authMiddleware(),
linkCreatorGuard((req) => req.query.linkId),
async (req, res) => {
await prisma.link.delete({
where: {
id: req.query.linkId
}
})
res.json({
message: "success",
});
}
);
Then add a delete mutation and a delete button on the page:
// pages/index.tsx
+async function deleteLink({ linkId }) {
+ await axios.delete(`/api/link/${linkId}`)
+}
function IndexPage(props: {
user?: {
name: string
}
}) {
const fetchAllLinksQuery = useQuery('fetchAllLinks', fetchAllLinks)
+ const deleteLinkMutation = useMutation(deleteLink, {
+ onSuccess() {
+ queryClient.invalidateQueries('fetchAllLinks')
+ },
+ onError(err) {
+ alert(err.response.data.message)
+ }
+ })
return (
<>
<div>
{props.user ? <>
<span>Hi, {props.user.name}, </span>
<a href="/api/logout">Logout</a>
</> : <>
<a href="/login">Login</a>
</>}
</div>
{/* Only signed in user can see the submit link form */}
{props.user && <div>
<SubmitLinkForm />
</div>}
<div>
{fetchAllLinksQuery.isLoading && <div>Loading...</div>}
{fetchAllLinksQuery.data?.map(link => {
return (
<div style={{ marginTop: '1rem' }}>
<div key={link.id}>
<a href={link.url}>{link.title}</a> <span>by: {link.creatorName}</span>
</div>
<div>
+ <button
+ disabled={deleteLinkMutation.isLoading}
+ onClick={_ => deleteLinkMutation.mutate({ linkId: link.id })}
+ >
+ delete
+ </button>
</div>
<div>
<EditLinkForm link={link} />
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</>
)
}
Delete a link that’s not created by me, I’ll get Permission Denined:
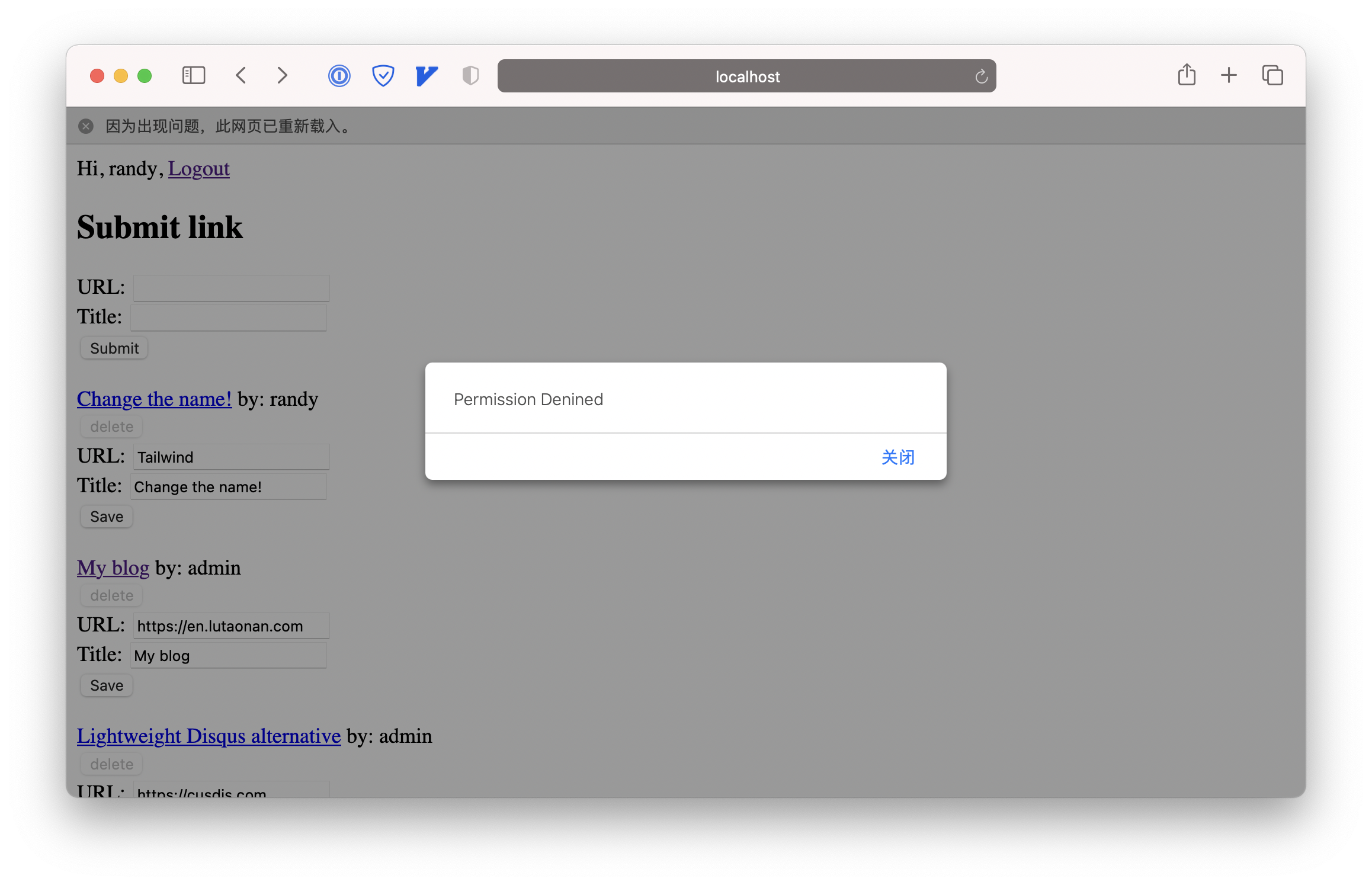
Delete my own link, the link disappear immediately from the links list: